CHILDREN ARE LOOSING THE ABILITY TO TALK
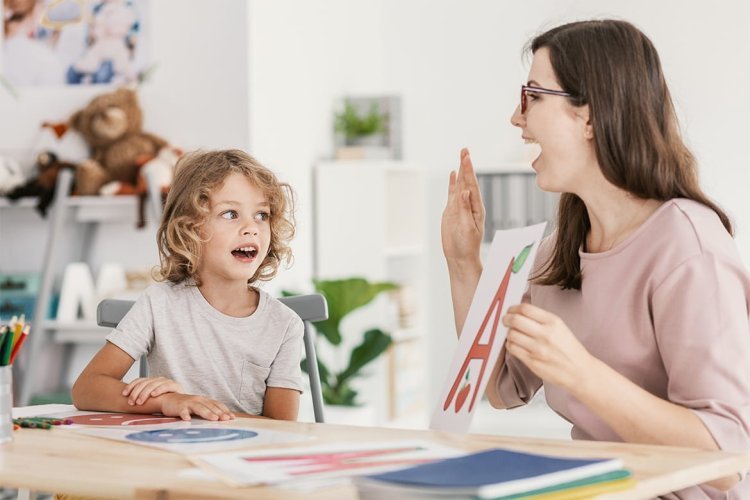

CHILDREN ARE LOOSING THE ABILITY TO TALK
Speech and language delays are becoming increasingly prevalent in children, a trend influenced by several environmental, social, and developmental factors. Some of the most significant factors include:
1. Excessive Screen Time: Early and prolonged exposure to screens (smartphones, tablets, etc.) reduces opportunities for children to engage in face-to-face communication and interactive play, which are crucial for speech and language development.
2. Reduced Social Interaction: Modern lifestyles often limit children's social experiences with peers and adults, reducing the natural opportunities for language practice and conversation.
3. Lack of Stimulating Language Environments: In homes where parents or caregivers are less engaged in verbal interaction with the child, the child misses out on hearing and practicing rich language patterns.
4. Parental Anxiety and Overcompensation: Some parents, worried about their child's development, may overcompensate by speaking for them or fulfilling their needs without encouraging verbal communication, which can further delay speech.
5. Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Conditions like Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), ADHD, and other learning disabilities can naturally cause speech and language delays. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial.
6. Hearing Impairments: Undetected hearing issues in children can hinder their ability to learn language effectively, leading to delays.
7. Bilingualism and Multilingualism: While being exposed to multiple languages can offer long-term cognitive benefits, some children may initially show delays in expressive language as they process and differentiate between languages.
8. Prematurity or Birth Complications: Children born prematurely or those with difficult deliveries might have developmental challenges that affect speech and language milestones.
Addressing these factors early on through interventions such as speech therapy, creating enriching language environments, and promoting face-to-face interaction can significantly improve outcomes for children with

 completetherapysolutions
completetherapysolutions